Web Audio API
API
BaseAudioContext
Also implements methods from the interface EventTarget.
createBuffer()
Creates a new, empty AudioBuffer object, which can then be populated by data and played via an AudioBufferSourceNode.
createConstantSource()
Creates a ConstantSourceNode object, which is an audio source that continuously outputs a monaural (one-channel) sound signal whose samples all have the same value.
createBufferSource()
Creates an AudioBufferSourceNode, which can be used to play and manipulate audio data contained within an AudioBuffer object. AudioBuffers are created using AudioContext.createBuffer or returned by AudioContext.decodeAudioData when it successfully decodes an audio track.
createScriptProcessor()
Creates a ScriptProcessorNode, which can be used for direct audio processing via JavaScript.
createStereoPanner()
Creates a StereoPannerNode , which can be used to apply stereo panning to an audio source.
createAnalyser()
Creates an AnalyserNode, which can be used to expose audio time and frequency data and for example to create data visualisations.
createBiquadFilter()
Creates a BiquadFilterNode, which represents a second order filter configurable as several different common filter types: high-pass, low-pass, band-pass, etc.
createChannelMerger()
Creates a ChannelMergerNode, which is used to combine channels from multiple audio streams into a single audio stream.
createChannelSplitter()
Creates a ChannelSplitterNode , which is used to access the individual channels of an audio stream and process them separately.
createConvolver()
Creates a ConvolverNode, which can be used to apply convolution effects to your audio graph, for example a reverberation effect.
createDelay()
Creates a DelayNode , which is used to delay the incoming audio signal by a certain amount. This node is also useful to create feedback loops in a Web Audio API graph.
createDynamicsCompressor()
Creates a DynamicsCompressorNode, which can be used to apply acoustic compression to an audio signal.
createGain()
Creates a GainNode, which can be used to control the overall volume of the audio graph.
createIIRFilter()
Creates an IIRFilterNode , which represents a second order filter configurable as several different common filter types.
createOscillator()
Creates an OscillatorNode, a source representing a periodic waveform. It basically generates a tone.
createPanner()
Creates a PannerNode , which is used to spatialise an incoming audio stream in 3D space.
createPeriodicWave()
Creates a PeriodicWave, used to define a periodic waveform that can be used to determine the output of an OscillatorNode.
createWaveShaper()
Creates a WaveShaperNode, which is used to implement non-linear distortion effects.
decodeAudioData()
Asynchronously decodes audio file data contained in an ArrayBuffer. In this case, the ArrayBuffer is usually loaded from an XMLHttpRequest’s response attribute after setting the responseType to arraybuffer. This method only works on complete files, not fragments of audio files.
resume()
Resumes the progression of time in an audio context that has previously been suspended/paused.
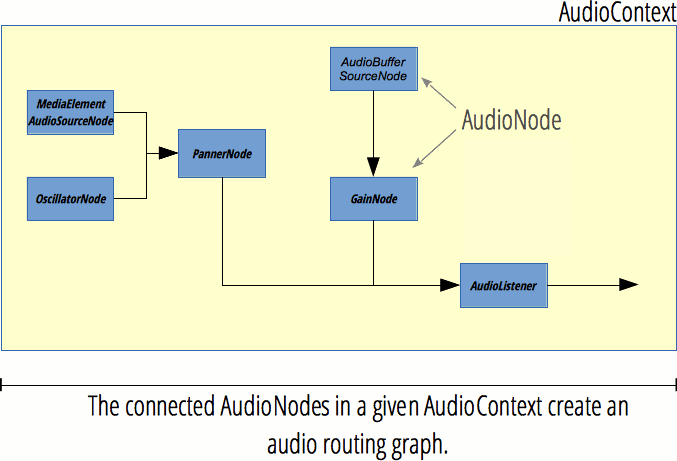
AudioContext
The AudioContext interface represents an audio-processing graph built from audio modules linked together, each represented by an AudioNode.
AudioContext 接口是一个音频处理图,它由音频模块连接在一起构成,每个音频模块是一个 AudioNode
An audio context controls both the creation of the nodes it contains and the execution of the audio processing, or decoding. You need to create an AudioContext before you do anything else, as everything happens inside a context. It’s recommended to create one AudioContext and reuse it instead of initializing a new one each time, and it’s OK to use a single AudioContext for several different audio sources and pipeline concurrently.
createMediaElementSource
Creates a MediaElementAudioSourceNode associated with an HTMLMediaElement. This can be used to play and manipulate audio from <video> or <audio> elements.
createMediaStreamSource
Creates a MediaStreamAudioSourceNode associated with a MediaStream representing an audio stream which may come from the local computer microphone or other sources.
createMediaStreamDestination
Creates a MediaStreamAudioDestinationNode associated with a MediaStream representing an audio stream which may be stored in a local file or sent to another computer.
createMediaStreamTrackSource
Creates a MediaStreamTrackAudioSourceNode associated with a MediaStream representing an media stream track.
AudioNode
The AudioNode interface is a generic interface for representing an audio processing module.
Examples include:
an audio source (e.g. an HTML <audio> or <video> element, an OscillatorNode, etc.),
the audio destination –> speaker
intermediate processing module (e.g. a filter like BiquadFilterNode or ConvolverNode), or
volume control (like GainNode)
Also implements methods from the interface EventTarget.
AudioNode.connect()
Allows us to connect the output of this node to be input into another node, either as audio data or as the value of an AudioParam.
AudioNode.disconnect()
Allows us to disconnect the current node from another one it is already connected to.
ScriptProcessorNode
ScriptProcessorNode 接口允许使用JavaScript生成、处理、分析音频. 它是一个 AudioNode, 连接着两个缓冲区音频处理模块, 其中一个缓冲区包含输入音频数据,另外一个包含处理后的输出音频数据.
实现了 AudioProcessingEvent 接口的一个事件,每当输入缓冲区有新的数据时,事件将被发送到该对象,并且事件将在数据填充到输出缓冲区后结束.
Event Handler
The onaudioprocess event handler of the ScriptProcessorNode interface represents the event handler to be called for the audioprocess event that is dispatched to ScriptProcessorNode node types.
An event of type AudioProcessingEvent will be dispatched to the event handler.
AudioProcessingEvent
InputBuffer
The buffer containing the input audio data to be processed.
The number of channels is defined as a parameter, numberOfInputChannels, of the factory method AudioContext.createScriptProcessor().
Note the returned AudioBuffer is only valid in the scope of the onaudioprocess function.
OutputBuffer
The buffer where the output audio data should be written. The number of channels is defined as a parameter, numberOfOutputChannels, of the factory method AudioContext.createScriptProcessor().
Note the returned AudioBuffer is only valid in the scope of the onaudioprocess function.
AudioBuffer
The AudioBuffer interface represents a short audio asset residing in memory, created from an audio file using the AudioContext.decodeAudioData() method, or from raw data using AudioContext.createBuffer().
Once put into an AudioBuffer, the audio can then be played by being passed into an AudioBufferSourceNode.
Objects of these types are designed to hold small audio snippets, typically less than 45 s. For longer sounds, objects implementing the MediaElementAudioSourceNode are more suitable.
The buffer contains data in the following format: non-interleaved IEEE754 32-bit linear PCM with a nominal range between -1 and +1, that is, a 32-bit floating point buffer, with each sample between -1.0 and 1.0. If the AudioBuffer has multiple channels, they are stored in separate buffers.
AudioBuffer.getChannelData()
Returns a Float32Array containing the PCM data associated with the channel, defined by the channel parameter (with 0 representing the first channel).
AudioBuffer.copyFromChannel()
Copies the samples from the specified channel of the AudioBuffer to the destination array.
AudioBuffer.copyToChannel()
Copies the samples to the specified channel of the AudioBuffer, from the source array.
FAQ
how to visualize audio wave
var audioCtx = new (window.AudioContext || window.webkitAudioContext)();
var analyser = audioCtx.createAnalyser();
source = audioCtx.createMediaStreamSource(stream);
source.connect(analyser);
analyser.connect(distortion);
distortion.connect(audioCtx.destination);
how to create an AudioBuffer and fill it with random white noise
var audioCtx = new (window.AudioContext || window.webkitAudioContext)();
// Create an empty three-second stereo buffer at the sample rate of the AudioContext
var myArrayBuffer = audioCtx.createBuffer(2, audioCtx.sampleRate * 3, audioCtx.sampleRate);
// Fill the buffer with white noise;
// just random values between -1.0 and 1.0
for (var channel = 0; channel < myArrayBuffer.numberOfChannels; channel++) {
// This gives us the actual array that contains the data
var nowBuffering = myArrayBuffer.getChannelData(channel);
for (var i = 0; i < myArrayBuffer.length; i++) {
// Math.random() is in [0; 1.0]
// audio needs to be in [-1.0; 1.0]
nowBuffering[i] = Math.random() * 2 - 1;
}
}
// Get an AudioBufferSourceNode.
// This is the AudioNode to use when we want to play an AudioBuffer
var source = audioCtx.createBufferSource();
// set the buffer in the AudioBufferSourceNode
source.buffer = myArrayBuffer;
// connect the AudioBufferSourceNode to the
// destination so we can hear the sound
source.connect(audioCtx.destination);
// start the source playing
source.start();